Chart of the month: June 2023
Share this insight
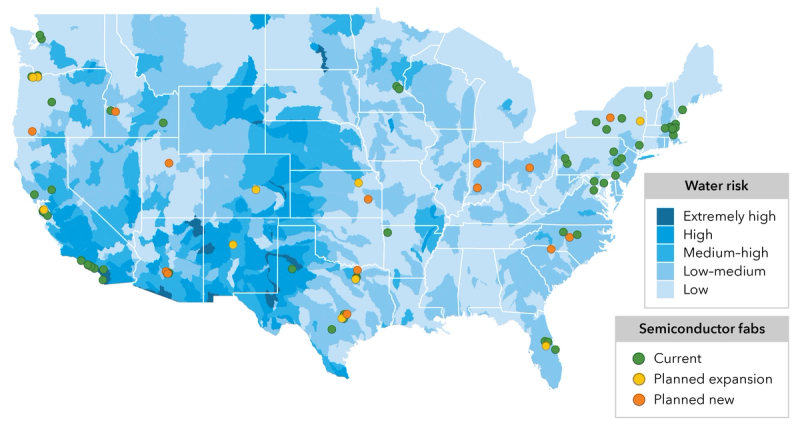
Source: SIA, World Resource Institute.
This month’s chart demonstrates the distribution of front-end manufacturing facilities for semiconductors (foundries and integrated device manufacturers) throughout the United States of America, alongside the distribution of water risk across the country.
The map shows that some industry hubs coincide with areas of high water risk; California, Arizona and Texas are renowned popular locations for large-scale semiconductor manufacturing facilities. Intel and Infineon own facilities in all three of these states, and Arizona hosts facilities owned by market leader TSMC, while Texas hosts Samsung Austin Semiconductor and Texas Instruments. Moreover, some facilities are located in areas of extremely high water risk, such as the X-Fab facility in Lubbock, Texas.
As worries over the climate crisis mount up and chips become smaller and more complex, selection of sites for future fabs is becoming critical. A reliable supply of water is crucial to the semiconductor manufacturing process, particularly as chips become smaller and more complex; increased process complexity leads to increased energy and water use, thereby intensifying the issue of water security.
Semiconductor manufacturing facilities tend to cluster near each other in certain cities and states. Clusters of fabs reflect the importance of an underpinning local infrastructure that can support a fab’s needs. Fabs situated in the vicinity of other facilities take advantage of access to pre-existing pools of talent, materials, and power, as well as close proximity to suppliers and end users.
Risk relating to environmental factors is another vital consideration in planning future fab locations – extreme weather conditions can grind chip production to a halt, as seen in Texas in the winter of 2021. Resource availability has significant implications for facility operations.
Accordingly, water availability affects a whole host of decisions in a fab, from operations to technology selection, and even budget. For example, the sequencing of water treatment might be optimized for conserving water if a fab is in an area of particular water scarcity, or for chemical conservation if in an area with plenty of available water. For more information relating to water scarcity and how this feeds into water treatment options watch the UPM Community Event from March 2023 on Environmental Sustainability.
Share this insight





